Every end user wants their final product more than they expect – start from play toys to life-saving medical devices. In other side of the world, the manufacturers are always trying to reduce the level of wastages during the process of manufacturing to get visible profit more than every yesteryear. To make the manufacturing industries lucrative and to mark the dimensions of the future needs, Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing, a household name) is already becoming norm in the industry.
Additive Manufacturing have been witnessed for its efficiency and efficacy in many 3D Printing markets, such as Consumer Electronics, Automotive Industries, Medical Device Industry, etc., Before getting deep dive into the future sea of 3D Printing, let’s just walk through in the landscape, in which Additive Manufacturing has printed its footsteps.
What is Additive Manufacturing?
As it name implies “Add”, it’s the process of adding layer upon layer of material. The technology can be stated as 3D design is converted into 3D object.
The process by which 3D design is converted into 3D object by adding layer upon layer of material is Additive Manufacturing.
The materials used in this process are plastic, metal, concrete, etc.
Evolution of Additive Manufacturing
Overcoming the disadvantages in an existing process will give rise to the new invention. From the evolution of Additive Manufacturing, we can know the longevity of 3D Printing as its process is effective and efficient.
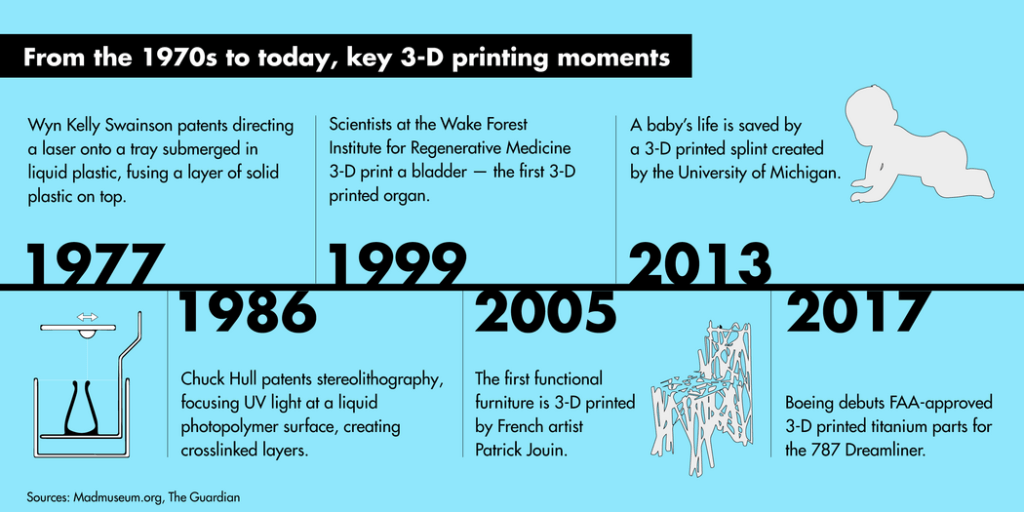
Rapid Prototyping(1988-1994)
We can generate only non-structural the demo pieces in Rapid prototyping; whereas in Additive Manufacturing, we can generate fully functional final components.
Rapid Tooling (1995-2003)
These are primarily used to create multiple prototypes. Rapid Tooling (RT) can be categorized as Soft Tooling and Hard Tooling.
- Soft Tooling: The moulds produced are destroyed either directly or indirectly after a single cast;
- Hard Tooling: The molds produced can be used for high volume of productions.
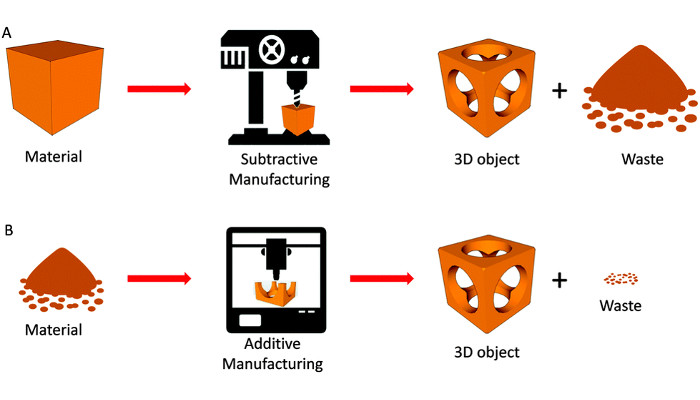
Additive Manufacturing than Subtractive Manufacturing (from 2005-Till Date)
One plus One is greater than Two – this formula works in deriving success equation of 3D Printing.
Rapid Tooling + Additive Manufacturing
As companies believe that the RT is the successful method for producing molds, they blend RT with the advances in Additive Manufacturing that wiped out the Subtractive Manufacturing process.
Fall of Subtractive Manufacturing
Rise of Additive Manufacturing
| Manual removal of material from an object | It add layers to create an object |
| More wastages | Less wastages |
| Difficult to design complex structures | Easy to design complex structures |
| Suits only in metal | Suits even for smaller items in plastics |
| More expensive | Less expensive |
Additive Manufacturing prints its footsteps in the Industries:
- Automotive;
- Medical & healthcare;
- Aerospace;
- Nano Manufacturing;
- Architecture;
- Biomedical implants
Techniques in Additive Manufacturing
From the materials used to build parts, we can categorize Additive Manufacturing as Direct & Indirect Techniques.
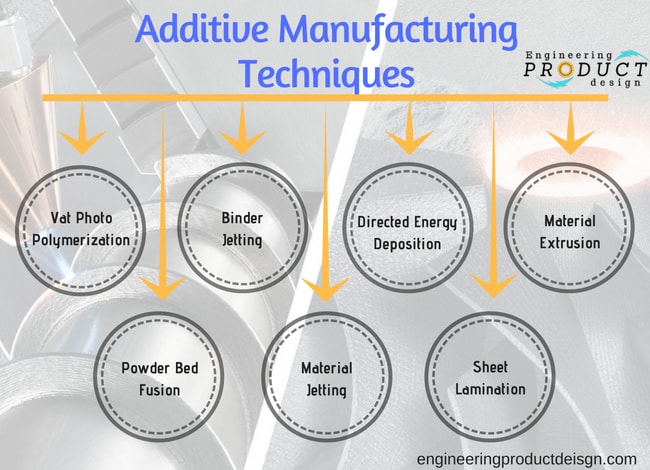
| Direct Additive Manufacturing Technique | Direct Additive Manufacturing Technique |
| Binder Jetting | Vat-photo polymerization |
| Powder Bed Fusion | Material jetting |
| Sheet Lamination | Material Extrusion |
| Directed Energy Deposition |
- Direct techniques use metal powder, sheets or wire with controlled Direct Metal Laser Melting (DMLM), Selective Laser Melting (SLM), LaserCUSING, and Electron Beam Melting (EBM) to build parts.
- Indirect techniques use plastics or binder then cast the metal part.
Future of Additive Manufacturing
Still you’re cynical with Additive Manufacturing—this is for your testament from Springer “Just as 3D CAD is becoming What You See Is What You Get (WYSIWYG), so it is the same with AM and we might just as easily say that What You See Is What You Build (WYSIWYB).”

I’d like to give you a fly on the wall information on real-time innovation using 3D printers that happened recently in Republic of China.
Chinese Firm used giant 3D Printers and printed ten houses—the cliffhanger ending is that they done it in just single day—BROUHAHA!
Significant efforts are taken to make the Additive Manufacturing as “business as usual” with its core strong areas “Complexity, Consolidation, and Customization”.
Recent statistics shows that there are >6 manufacturers call for 3D Printing out of 10 numbers—JABIL Report.
Current state of things reflect the percentage of adopting 3D Printing in manufacturing process is increasing as “two-thirds of manufactures already using 3D printing & 25% planned to adopt”, stated in UPS and the consumer report.
By and large—rain or shine, the future of Additive Manufacturing is undoubtedly a go-to option for manufacturers at the expense of its quality, less consuming factor, less wastage, capable of doing complex structures, etc.